Logic gates or circuits are devices that operate and work with one or more logic input signals to produce one and only one output, depending on the function implemented in the circuit.
The situations “Truth” and “False” are studied in the Mathematical Logic or Boole Logic. There are the following logic gates: AND, OR and NOT are the main ones, because with them we can form the others that are: NAND, NOR, XOR and XNOR.
Remembering that when analyzing execution output: 0 is true (without error) and 1 is false ( >= 1 is error ), so this can confuse your mind when analyzing the examples, as it is the other way around, but I will not invert because it is as soon as it is in reality, then we will use the concept of computation and not execution output: 0 as false and 1 is true. 😃
AND logical_and
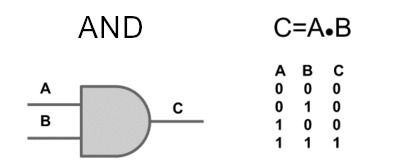
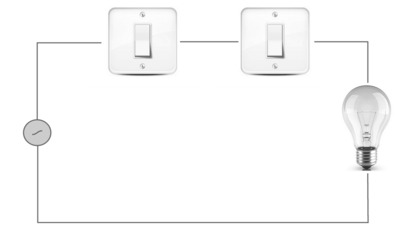
This port results in a true logical value only if all operators have a true value (in this case it is 1). An idea of understanding would be two switches connected in series) and a lamp at the end, that is, the lamp will only be switched on if these two switches are on.
For these examples we will use the std::transform function. Let’s analyze the output of the combination of two arrays using std::logical_and:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
int main(){
const int num = 3;
bool array1[] = { false, false, true },
array2[] = { false, true, true },
result[ num ];
std::transform( array1, array1 + num, array2, result, std::logical_and<bool>());
std::cout << "Logic AND:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i){
std::cout << array1[i] << " AND " << array2[i] << " = " << result[i] << "\n";
}
return 0;
}The output will be:
0 AND 0 = 0
0 AND 1 = 0
1 AND 1 = 1If you want to see the literal output, use this:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
int main(){
const int num = 3;
bool array1[] = { false, false, true },
array2[] = { false, true, true },
result[ num ];
const char * vf;
std::transform( array1, array1 + num, array2, result, std::logical_and<bool>());
std::cout << "Logic AND:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i){
vf = ( result[i] == 0 ? "false" : "true" );
std::cout << array1[i] << " AND " << array2[i] << " = " << vf << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
The output will be:
Logic AND:
0 AND 0 = false
0 AND 1 = false
1 AND 1 = trueThat is, just like the example of the lamps, only if both are true that the output is true!
NOT logical_not
The NOT or inverter port is a digital logic port that implements logical negation, according to the truth table below. That is, if it is false it returns true and if it is true it returns false.
In this example we will use only one array (only with 2 elements) and of course we will only pass 4 parameters to
std::transform.
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
int main(){
const int num = 2;
bool array1[] = { false, true },
result[ num ];
const char * vf;
std::transform( array1, array1 + num, result, std::logical_not<bool>());
std::cout << "Logic NOT:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i){
vf = ( result[i] == 0 ? "false" : "true" );
std::cout << array1[i] << " NOT" << " = " << vf << "\n";
}
return 0;
}The output will be:
Logic NOT:
0 NOT = true
1 NOT = false
OR logical_or
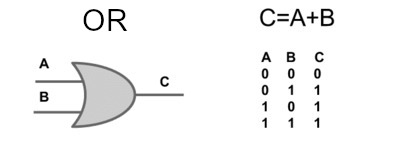
The OR logic gate is also called a logical disjunction, it is a logical operation between two or more operands that results in a false logical value if, and only if, all operands have a false value.
That is, if all values are false it will be false, otherwise it will be true.
Returning to the example of analyzing 2 arrays.
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
int main(){
const int num = 3;
bool array1[] = { false, false, true },
array2[] = { false, true, true },
result[ num ];
const char * vf;
std::transform( array1, array1 + num, array2, result, std::logical_or<bool>());
std::cout << "Logic OR:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i){
vf = ( result[i] == 0 ? "false" : "true" );
std::cout << array1[i] << " OR " << array2[i] << " = " << vf << "\n";
}
return 0;
}The output will be:
Logic OR:
0 OR 0 = false
0 OR 1 = true
1 OR 1 = trueThat’s it for today, they are small daily doses that will always keep us tuned in to C++!