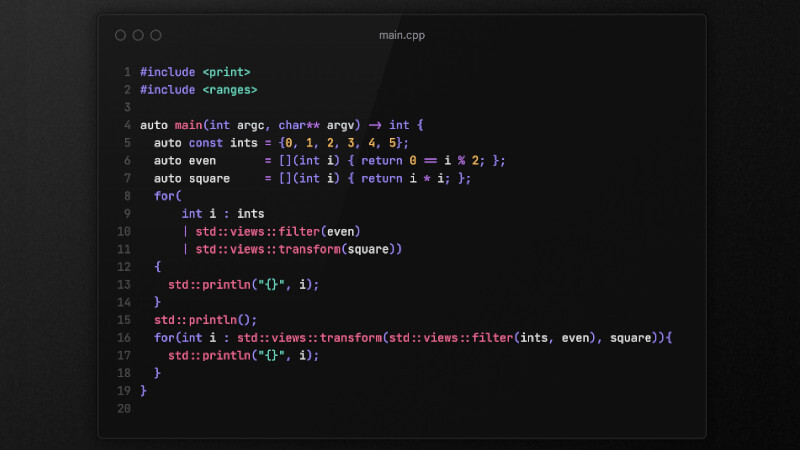
The for ranged-based loop was introduced from C++11 and has a slightly better performance. It is not always a case to be used, but whenever you can use it! For programmers of other languages loop for ranged-based can be compared to foreach.
In today’s cpp::daily we will show you 5 examples that will facilitate your understanding so you can use them whenever necessary!
01. Foreach style
for( int i : { 11, 2, 9, 17, 89, 12, 13, 52, 8, 4 } ){
std::cout << i << '\n';
}02. With vectors and automatic types
std::vector<int> vec = { 11, 2, 9, 17, 89, 12, 13, 52, 8, 4 };
for( auto &elem : vec ){
std::cout << elem << '\n';
}
03. When switched to function templates
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
template <typename T>
void print( const T& coll ){
for( auto &elem : coll ){
std::cout << elem << ' ';
}
std::cout << '\n';
}
int main(){
std::vector<int> vec = { 11, 2, 9, 17, 89, 12, 13, 52, 8, 4 };
print( vec );
return 0;
}04. Range based on vector declarations
std::vector<int> vec = { 11, 2, 9, 17, 89, 12, 13, 52, 8, 4 };
for ( auto pos = vec.begin(); pos != vec.end(); ++pos) {
std::cout << *pos << '\n';
}05. Adding elements in foreach style
int array[] = { 1, 2, 3 };
long sum = 0;
for ( int x : array ) {
sum += x;
}
for ( auto elem : { sum, sum * 2, sum * 4 } ) {
std::cout << elem << '\n';
}