Concept
According to wikipedia: A patch is a computer program created to update or correct software in order to improve its usability or performance. When patches fix bugs or security vulnerabilities, it is called a bugfix.
This technique can be used as one of the ways to distribute a software release. It is widely used in computer games in order to update the available content.
The
patchUNIX command: A patch (Unix) is a computer program on the UNIX operating system that applies the textual differences between two programs and, more often, to computer files containing those differences, or diff files.
According to manual: patch takes a patch file:
patchfilecontaining a difference list produced by the diff program and applies those differences to one or more original files, producing versions.
Normally, corrected versions are put in place of the original.
Syntax
patch [file you want to patch] [the patch]Practical example
Suppose you have the following file in C++:
vim hello.cpp
#include <iostream>
int main( int argc , char **argv ){
std::cout << "Hello World!" << '\n';
return 0;
}And then you create a new one based on it and change a few things:
cp hello.cpp new_hello.cpp
vim new_hello.cpp
#include <iostream>
int main( int argc , char **argv ){
std::cout << "Hello World!" << '\n';
std::cout << "It's a good world to end ..." << '\n';
return 0;
}When you run the command diff with the parameter -u you and generate a patch file: file.patch:
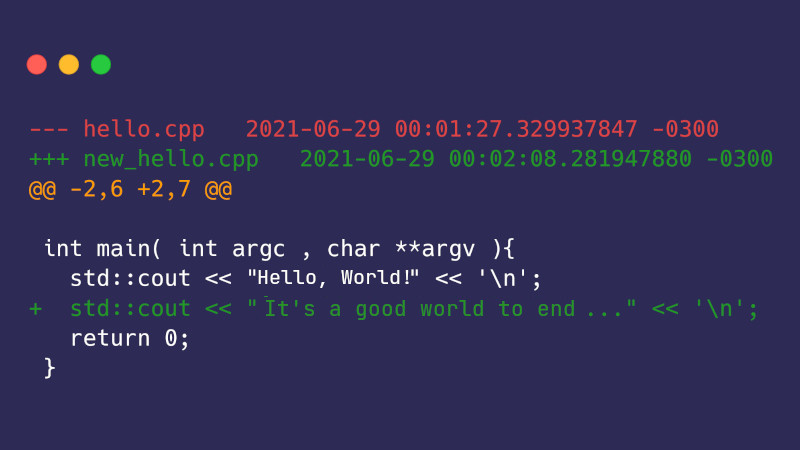
diff -u hello.cpp new_hello.cpp > file.patchAnd then the contents of file.patch will have the following code:
--- hello.cpp 2021-06-29 00:01:27.329937847 -0300
+++ new_hello.cpp 2021-06-29 00:02:08.281947880 -0300
@@ -2.6 +2.7 @@
int main( int argc , char **argv ){
std::cout << "Hello World!" << '\n';
+ std::cout << "It's a good world to end ..." << '\n';
return 0;
}Although this example is basic and you can change the line manually, in most cases on larger projects it would be a lot of work.
So, to apply the patch, as we saw in its Syntax above, just run the patch command:
patch hello.cpp file.patchAnd if you look at the contents of hello.cpp you will now see that it is identical to that of new_hello.cpp.
Easy, huh? Of course, there are still a lot of options and it’s worth taking a look at the manual and help:
patch --help
man patchSee too
Command cp with Progress Bar
Just applying a patch.