std::array is a C++ standard library container that stores a fixed number of elements of the same type in a single contiguous data structure in the memory. It is similar to a C++ native array, but with additional features and greater security.
The ideal is to abandon the C style of creating arrays and use std::array.
// bad idea
int arr[4] = {1, 2, 3, 4};Benefits of std::array
std::array is an attractive option for storing a fixed number of elements in a C++ program. Some benefits of using std::array over other containers include:
- Fixed size: The size of the array is determined at compile time and cannot be changed at runtime. This allows contiguous allocation of memory to array elements, which can result in better performance and memory efficiency.
- Increased security:
std::arrayprovides index bounds checking at runtime, which means that an error will be thrown if you try to access an element outside the bounds of the array. This helps to avoid common programming errors such as improper memory access. - Compatibility with the interface of other resources.
How to use std::array
To use std::array in a C++ program, you must include the <array> library and define an object of type std::array with your specified size and element type. For example:
std::array<int, 4> arr = {1, 2, 3, 4};Similar to the array created above in C.
To print the elements, for example:
for(auto &var : arr){
std::cout << var << '\n';
}Or use the traditional
loop.
You can also initialize the elements later, for example:
// Automatically all elements are initialized with ZERO value
std::array<int, 4> arr;
// It can be like this, to element zero in this case
arr[0] = 1;
// Or like this, to element 1 in this case
arr.at(1) = 2;When printing all the other elements that have not been defined, they will have a value equal to ZERO:
0.
Resources
std::array has several member functions and iterators to make it easier to use, for example:
Check if the array is empty with .empty():
std::cout << "The array is empty? " <<
( arr.empty() ? "Yes" : "No") << '\n';Among others as shown below:
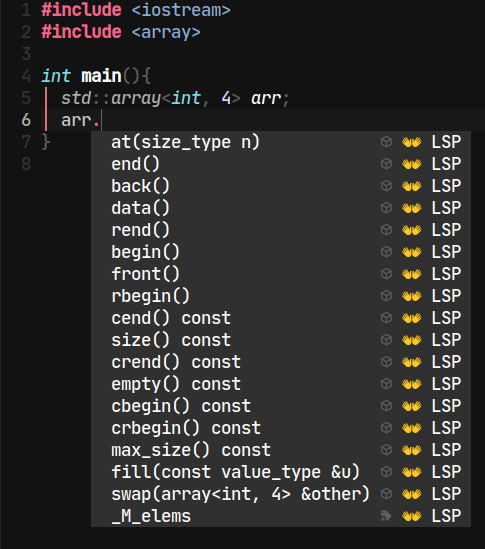
For more information see this link.