The
It has the following functions:
setiosflags- Defines flags formatresetiosflags- Resets flags formatsetbase- Sets the base of the flagssetfill- Defines the filling of characterssetprecision- Sets the precision of decimalssetw- Sets the width of a fieldget_money- Gets the monetary valueput_money- Insert the monetary valueget_time- Get the time and dateput_time- Get the time and date
Some examples
setfill and setw
Fill with a certain character on the left side of the number(int, float, double,…)
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
int main(){
std::cout << std::setfill (' ') << std::setw( 10 );
std::cout << 3.69f << '\n';
return 0;
}Filled with 6 blank spaces(10 minus the number of characters), so the output will be:
3.69. If we changestd::setfill (' ')tostd::setfill ('-')the output will be: ——3.69 .
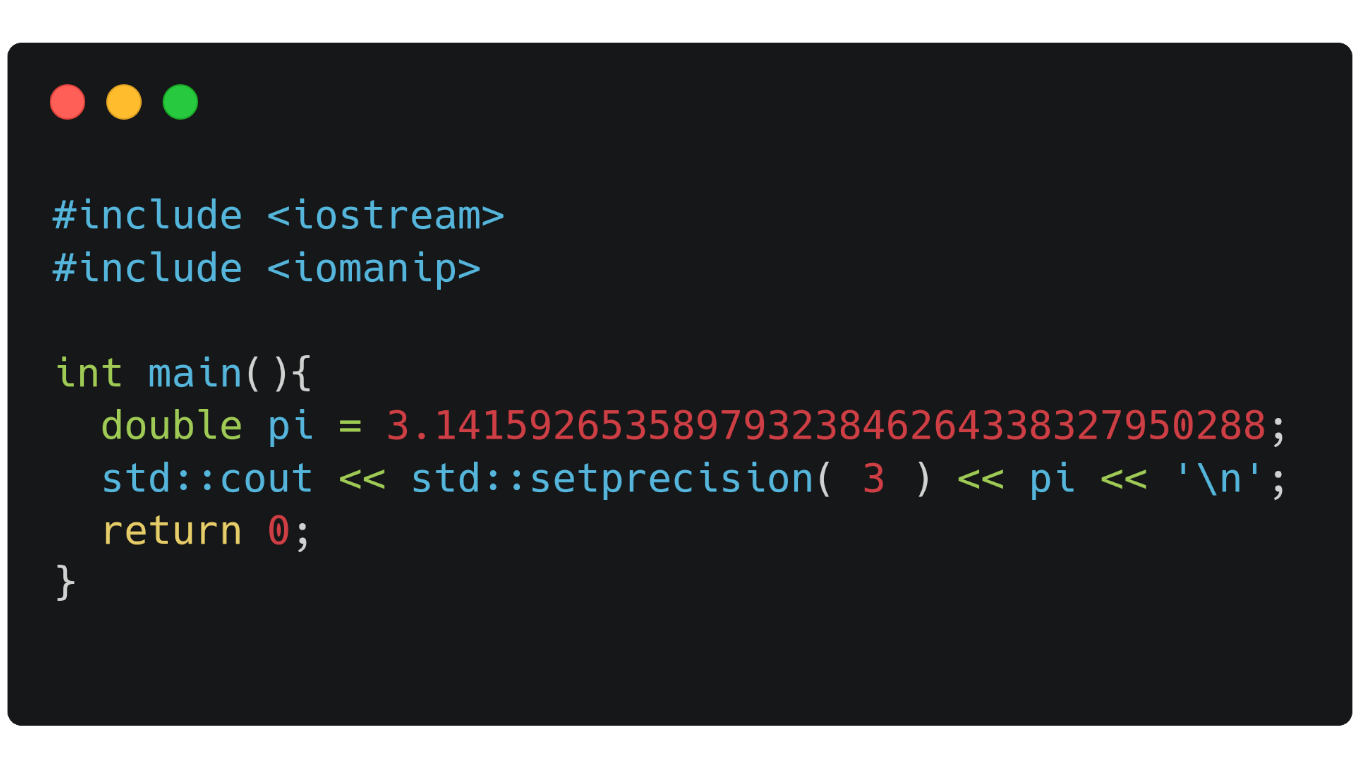
setprecision
Defines how many digits you want to appear if there is no more after the comma ( in this case, point . ), it will fill with 0 zeros if we use std::fixed .
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
int main(){
double pi = 3.14159;
std::cout << std::setprecision( 3 ) << pi << '\n';
return 0;
}Output:
3.14
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
int main(){
double pi = 3.14159;
std::cout << std::setprecision( 4 ) << pi << '\n';
return 0;
}Output:
3.142because the next significant number is equal to or greater than 5, so it approximates the previous one.
And if you change it to std::setprecision( 9 ), the output will be: 3.14159 will not complete with zeros, but using std::fixed
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
int main(){
double pi = 3.14159;
std::cout << std::fixed << std::setprecision( 9 ) << pi << '\n';
return 0;
}The output will be:
3.141590000
get_money and put_money
Informs the value in integer, in other words transforms: float, double,… in integer. They are useful for use with data entry. Example:
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
int main() {
long double preco;
std::cout << "Enter the price: ";
std::cin >> std::get_money( preco );
if( std::cin.fail() ){
std::cerr << "Failed to read price." << '\n';
return 1;
}else{
std::cout << "The price is: " << std::put_money( preco ) << '\n';
}
return 0;
}get_time
Formats the time entry, example:
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <ctime> // struct std::tm
int main(){
struct std::tm dthr;
std::cout << "Enter the time: ";
std::cin >> std::get_time(&dthr,"%R"); //extract the hours in 24H format
std::cout << "It's " <<
dthr.tm_hour << " hours and "
<< dthr.tm_min << " minutes\n";
return 0;
}Output:
Enter the time: 12:23
It's 12 hours and 23 minutes