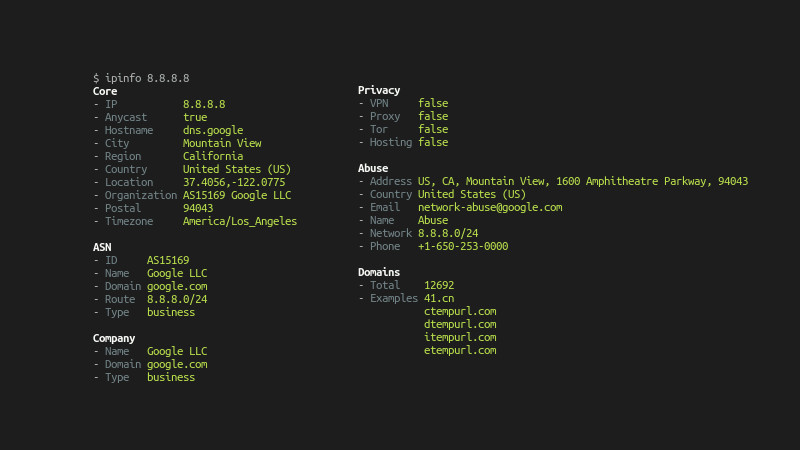
The math behind IP addresses is complicated. Good IPv4 addresses start as 32-bit binary numbers, which are converted to 10 base numbers in four 8-bit fields. Decimal numbers are easier to manage than long binary strings.
Still, calculating address ranges, netmasks, and subnets is a bit difficult and error-prone, except for brainiacs that can do binary conversions in their heads. For the rest of us, answer ipcalc and ipv6calc.
ipcalc is for IPv4 networks and ipv6calc is for IPv6 networks. You must understand Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR), as this is critical to IP addressing.
Installation
Both ipcalc and ipv6calc are available in most repositories of Linux distributions and BSD systems. See the procedure for each:
emerge net-misc/ipcalc # Gentoo, Funtoo e derivados
sudo apt install ipcalc # Ubuntu, Debian e Mint
sudo pacman -S ipcalc # Arch Linux, Manjaro e outros
sudo yum install ipcalc # Red Hat e CentOS
sudo dnf install ipcalc # FedoraApós instalar o modo básico de calcular é:
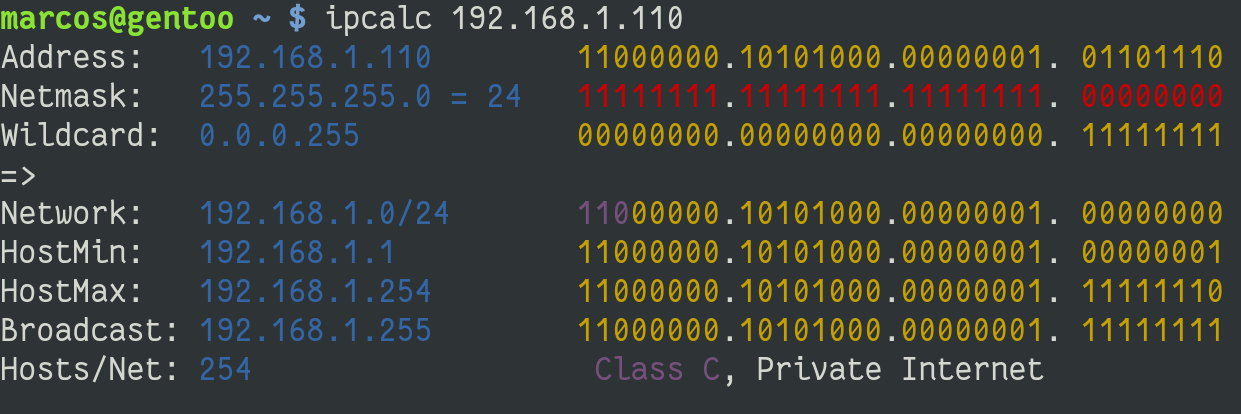
ipcalc 192.168.1.110The output will be
Address: 192.168.1.110 11000000.10101000.00000001. 01101110
Netmask: 255.255.255.0 = 24 11111111.11111111.11111111. 00000000
Wildcard: 0.0.0.255 00000000.00000000.00000000. 11111111
=>
Network: 192.168.1.0/24 11000000.10101000.00000001. 00000000
HostMin: 192.168.1.1 11000000.10101000.00000001. 00000001
HostMax: 192.168.1.254 11000000.10101000.00000001. 11111110
Broadcast: 192.168.1.255 11000000.10101000.00000001. 11111111
Hosts/Net: 254 Class C, Private InternetThat is, it will display the data as:
- Address: Displays the address you searched for and the binary ID separated by octets;
- Wildcard: Indicates which parts of an IP address are available for examination.
- Netmask: Shows the mask;
- Broadcast: The last valid IP address for the network that has the IP you searched for.
And among other data and options that can be further expanded, see the command help for more information:
ipcalc --help
If you want to make consultations online, ipcalc makes the web version available at: http://jodies.de/ipcalc