A while ago I had created a script in Bash(Shell Script) which cleaned up some things on my system, including:
- The cache of images that were viewed, including thumbnails;
- The cache of the browsers I had installed on my machine: Google Chrome, Firefox and Opera;
- History with Bash;
- Recent files;
- And the trash can!
The script worked normally, I just had to run the limpeza command in terminal.
However, one fine day when I ran this script, I noticed that it took a long time to execute. The reason for this was that in the trash there were several .iso files, together I think they were about 5GB in size!
And then I thought asking myself:
— Why did Bash take so long to remove???
And I think:
— If I wrote this script in C++, would it take so long?!
So, I decided to do it and test it! After finishing writing, I deleted about 10GB of .iso (I threw it in the trash) and ran the post-compiled code to test with the command time and compared the result of the same command with that of the Bash script.
And the difference was BIG! In other words, the same script made in C++ was much faster!
Well, it’s been a long time, but I decided to post it here, because this “script” serves as an exercise for those who are training their C++ codes, it’s a good idea to use: C++ as Shell Script to improve your skills!
Writing the code
As we are going to compile with CMake, the ideal is to create a folder for the project:
mkdir cleanup
cd cleanup
All files
cleanup.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <filesystem>
#include <memory>
#include <array>
#include <fstream>
#include "colors.hpp"
namespace fs = std::filesystem;
class Cleanup {
bool m_debug;
std::string m_path;
const std::string m_home = std::getenv("HOME");
const fs::path m_trash = ".local/share/Trash/files";
const fs::path m_thumbs = ".cache/thumbnails";
const fs::path m_chrome = ".cache/google-chrome";
const fs::path m_fox = ".cache/mozilla";
const fs::path m_opera = ".cache/opera";
const fs::path m_recent = ".local/share/recently-used.xbel";
const fs::path m_bash_h = ".bash_history";
protected:
void print(bool, const std::string&);
bool clean_dir(const std::array<std::string, 3>& = {});
bool clean_file(const std::array<std::string, 3>& = {});
public:
Cleanup(bool);
void run();
};
colors.cpp
#ifndef COLORS_H
#define COLORS_H
#include <iostream>
namespace hey {
const std::string gray = "\033[30;10m", // normal
grayn = "\033[30;1m", // bold
grayf = "\033[30;2m", // weak
grayi = "\033[30;3m", // italics
grays = "\033[30;4m", // underline
grayp = "\033[30;5m", // blinking
grayb = "\033[30;7m", // background
grayc = "\033[30;9m", // canceled
red = "\033[31;10m", // normal
redn = "\033[31;1m", // bold
redf = "\033[31;2m", // weak
redi = "\033[31;3m", // italics
reds = "\033[31;4m", // underscore
redp = "\033[31;5m", // flashing
redb = "\033[31;7m", // background
redc = "\033[31;9m", // canceled
green = "\033[32;10m", // normal
greenn = "\033[32;1m", // bold
greenf = "\033[32;2m", // weak
greeni = "\033[32;3m", // italics
greens = "\033[32;4m", // underline
greenp = "\033[32;5m", // blinking
greenb = "\033[32;7m", // background
greenc = "\033[32;9m", // canceled
yellow = "\033[33;10m", // normal
yellown = "\033[33;1m", // bold
yellowf = "\033[33;2m", // weak
yellowi = "\033[33;3m", // italics
yellows = "\033[33;4m", // underlined
yellowp = "\033[33;5m", // blinking
yellowb = "\033[33;7m", // background
yellowc = "\033[33;9m", // canceled
blue = "\033[34;10m", // normal
bluen = "\033[34;1m", // bold
bluef = "\033[34;2m", // weak
bluei = "\033[34;3m", // italics
blues = "\033[34;4m", // underline
bluep = "\033[34;5m", // blinking
blueb = "\033[34;7m", // background
bluec = "\033[34;9m", // canceled
purple = "\033[35;10m", // normal
purplen = "\033[35;1m", // bold
purplef = "\033[35;2m", // weak
purplei = "\033[35;3m", // italics
purples = "\033[35;4m", // underline
purplep = "\033[35;5m", // blinking
purpleb = "\033[35;7m", // background
purplec = "\033[35;9m", // canceled
cyan = "\033[36;10m", // normal
cyann = "\033[36;1m", // bold
cyanf = "\033[36;2m", // weak
cyani = "\033[36;3m", // italics
cyans = "\033[36;4m", // underscore
cyanp = "\033[36;5m", // blinking
cyanb = "\033[36;7m", // background
cyanc = "\033[36;9m", // canceled
white = "\033[38;10m", // normal
whiten = "\033[38;1m", // bold
whitef = "\033[38;2m", // weak
whitei = "\033[38;3m", // italics
whites = "\033[38;4m", // underscore
whitep = "\033[38;5m", // blinking
whiteb = "\033[38;7m", // background
whitec = "\033[38;9m", // canceled
off = "\033[m"; // turns off
}
#endif
cleanup.cpp
#include "cleanup.hpp"
Cleanup::Cleanup(bool debug) : m_debug(debug){
m_path = {};
}
void Cleanup::run(){
this->clean_dir({m_trash, "Recycle bin emptied", "empty trash"});
if(m_debug){ std::cout << hey::yellow << m_path << hey::off << "\n\n";}
this->clean_file({m_recent, "Recent files cleaned", "clean recent files"});
if(m_debug){ std::cout << hey::yellow << m_path << hey::off << "\n\n";}
this->clean_file({m_bash_h, "Bash history removed", "clear Bash history"});
if(m_debug){ std::cout << hey::yellow << m_path << hey::off << "\n\n";}
this->clean_dir({m_thumbs, "Thumbnails removed", "remove Thumbnails cache"});
if(m_debug){ std::cout << hey::yellow << m_path << hey::off << "\n\n";}
this->clean_dir({m_chrome, "Chrome cache cleaned", "remove Chrome cache"});
if(m_debug){ std::cout << hey::yellow << m_path << hey::off << "\n\n";}
this->clean_dir({m_fox, "Firefox cache cleared", "remove Firefox cache"});
if(m_debug){ std::cout << hey::yellow << m_path << hey::off << "\n\n";}
this->clean_dir({m_opera, "Opera cache cleaned", "remove Opera cache"});
if(m_debug){ std::cout << hey::yellow << m_path << hey::off << "\n\n";}
}
void Cleanup::print(bool action, const std::string& msg){
(action) ?
std::cout << hey::green + "\u2705 " + msg + "!" + hey::off << '\n' :
std::cerr << hey::red + "\u274C Failed to " + msg + "." + hey::off << '\n';
}
bool Cleanup::clean_dir(const std::array<std::string, 3>& arr){
m_path = m_home + '/' + arr[0];
if(m_debug){
this->print(true, arr[1]);
return true;
}
try {
if (fs::exists(m_path) && fs::is_directory(m_path)) {
if (fs::is_empty(m_path)) {
return false;
}else{
if(fs::remove_all(m_path)){
this->print(true, arr[1]);
fs::create_directory(m_path);
}else{
this->print(false, arr[2]);
return false;
}
}
}else{
return false;
}
}catch (const fs::filesystem_error& e){
std::cerr << "PERFORM THIS ACTION: " << e.what() << '\n';
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool Cleanup::clean_file(const std::array<std::string, 3>& arr){
m_path = m_home + '/' + arr[0];
if(m_debug){
this->print(true, arr[1]);
return true;
}
try {
if (fs::exists(m_path) && fs::is_regular_file(m_path)) {
std::size_t size = std::filesystem::file_size(m_path);
if(size == 0){
return false;
}
if(fs::remove_all(m_path)){
this->print(true, arr[1]);
std::ofstream out(m_path);
out.close();
}else{
this->print(false, arr[2]);
return false;
}
}else{
return false;
}
}catch (const fs::filesystem_error& e){
std::cerr << "PERFORM THIS ACTION: " << e.what() << '\n';
return false;
}
return true;
}
main.cpp
#include "cleanup.hpp"
int main(int argc, char** argv){
bool debug {false};
if(argc > 1){
std::string param = argv[1];
if(param == "--debug"){
debug = true;
}else{
std::cerr << "Use: " << argv[0] << " [--debug]\n";
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
}
auto lp = std::make_unique<Cleanup>(debug);
lp->run();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Compiling with CMake, running and installing
To compile we will use this CMakeLists.txt:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.10)
set_property(GLOBAL PROPERTY INTERPROCEDURAL_OPTIMIZATION TRUE)
project(Cleanup
LANGUAGES CXX
VERSION 0.0.1
)
add_compile_options(-g -Wall -Wextra -Wpedantic -pedantic)
if(CHECK_MEM)
message("Compiling with libasan. Learn more: <https://github.com/google/sanitizers/>")
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -fsanitize=address")
endif()
set (CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 23)
add_executable(cleanup main.cpp cleanup.cpp)
Note in CMakeLists.txt that we can pass the optional parameter: -DCHECK_MEM=ON to use libasan which is the library: Google sanitizers, for more information see the video: 10 Flags and Parameters Tips for GNU GCC.
If you want to download all files click on the button below to download cleanup.zip:
So you can use CMake like this (with libasan):
cmake -B build . -DCHECK_MEM=ON
Or just:
cmake -B build .
Then compile and test with debug mode:
cmake --build build
build/clean --debug
If you want to install and use it to do your cleanup, I recommend using it locally (only for your user):
mkdir -p ~/.local/bin
echo 'export PATH="${PATH}:${HOME}/.local/bin" >> ~/.bashrc'
exec $SHELL
install -v ./build/cleanup ~/.local/bin
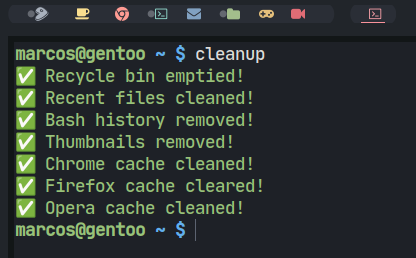
Test again to see everything that will or will not be removed and then run it definitively:
Remembering that without being in
debug mode, only the actions it executes will be output. For example, you don’t have Opera installed, or you’ve already run the command before, it won’t do anything or display it!
cleanup
Output:
If you want the terminal history to be clean after running everything, add an alias like this:
vim ~/.bashrcand paste this code at the end of the file:cleanup(){ ${HOME}/.local/bin/cleanup $@ history -c }And run:
exec $SHELLorsource ~/.bashrcDo it this way, as running processes like this with
std::systemnot only doesn’t work, it’s not recommended!
In the future I intend to show other scripts that I made with C++ and then organize them all and put them in a single repository on GitHub.
I hope you enjoyed this mini-adventure! 😎
cpp bash shellscript commands cppdaily